Offline Data Support
Offline support for mobile applications can be thought of as the ability of the application to react gracefully to the lack of stability in the network connection. It includes:
- App should work even when not connected to any network.
It is true for mobile apps for on-the-move users and for users working out of remote areas. In this context, one of the most complicated scenarios include “offline data access”.
Why offline data support
If the mobile app cannot communicate to the back-end server due to lack of network connection, the app turns to offline mode. In offline mode, app user cannot perform any action and forces user to wait when network connection gets back. This inability of a mobile app to work offline results in potential loss of time and business for the app user. To facilitate offline access to app users, app developers spend a lot of time and effort in redesigning the apps.
WaveMaker is providing offline data support as an out-of-the-box feature so that developers can enable offline support to existing components.
How Offline Support works in WaveMaker
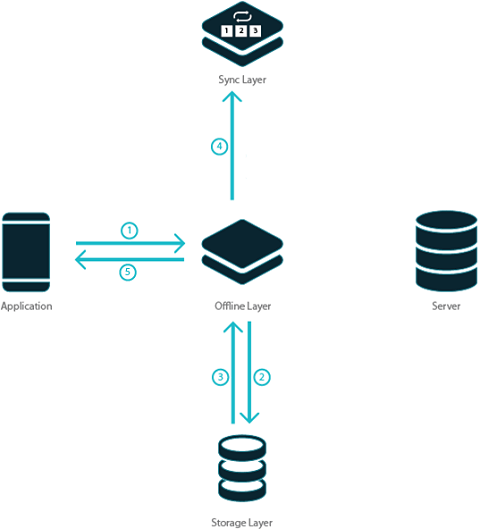
To enable offline data support, WaveMaker has a built-in offline layer.
- When app is online, it gets data from server and saves it for offline use.
- When the app is offline, the saved data is used to answer all data requests.
- When the app is offline, all changes done by the user are recorded.
- When the app comes online, offline data changes are pushed to the server.
The offline layer intercepts all data requests. When the app is online, it forwards the request to the server and receives the responses from the server. When the app is offline, it consumes the request and provides the response. The offline layer includes:
- Storage layer used to store data and answer all data calls from Variables based on Database CRUD APIs.
- Sync layer used to pull data from the server and push data changes to the server.
At the time of developing a mobile app in WaveMaker, you can define the database entities that need to be available in offline mode so as to enhance app performance.
App Behavior when Online
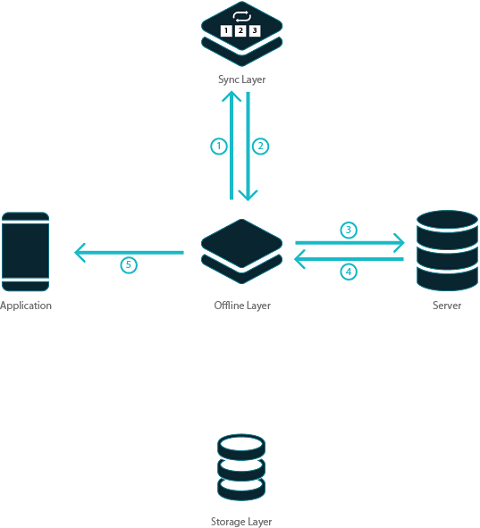
- An API call on behalf of a Database CRUD Variable to an entity is intercepted by the offline layer.
- This call is forwarded to the server.
- The server returns the entity data corresponding to the API call.
- The offline layer stores the data sent by the server in its storage layer.
- The entity data is forwarded as the response to the app.
- A data modification request through a Database CRUD Variable is received by the offline layer.
- This request is forwarded to the server.
- The entity data is returned by the server.
- The offline layer updates its storage layer.
- The data is forwarded as a response to the app.
App Behavior when Offline
- An API call on behalf of a Database CRUD Variable to an entity is intercepted by the offline layer.
- This request is forwarded to the storage layer (since the server is not reachable).
- The entity data is received from the storage layer.
- This data is forwarded as a response to the app.
- A data modification request is intercepted by the offline layer through a call to Database CRUD Variable,
- The corresponding entity in the storage layer is updated.
- The entity data from storage layout received by the offline layer.
- The data modification request is added to the queue within the sync layer.
- The data prepared by the storage layer is sent as a response to the app.
Thus, all data modification requests are added to the sync layer queue.
App Behavior when it comes back Online:
- When the app comes online push is initiated.
- All data modification requests from the sync layer queue are retrieved and
- sent to server synchronously.
- Once the response is received and the sync queue is cleared,
- the app gets restarted.
How Offline Storage Layer gets Data
WaveMaker uses an inbuilt SQL Lite Database for offline storage. Offline storage layer gets its data in 3 ways:
- Data bundled along with the installer (apk or ipa)is always available for offline. This will be helpful when a huge amount of data is needed in offline all the time. There are two settings available in this case:
- Bundle with installer - This option gives read-only access to the data. This option is particularly useful when giving the salesperson access to company's inventory list. If there is a possibility of this list getting updated intermittently, there is provision to set a timestamp-based field to allow for selective pulls.
- Bundle with installer with on-demand sync - This option gives a read-write access to the data. Data is bundled with the installer at the same time user can modify the data and sync the data. This option can be used when a company executive needs to add to the company's inventory list.
- Get data during app startup from the app-level Database CRUD Variables. The page level Database CRUD Variables are triggered only when the user visits the page. Unless the user visits a page once, data required for that page will not be available in offline. Say an app has with pages for employee and department details. The user opened the app and visited department page and closed the app. In offline mode, the user sees department page alone and employees page is not available as offline data for employees is not available. To deal with such scenarios, WaveMaker provides on-demand sync option to retrieve the required data during app runtime (by default at app startup).
- Accumulating data received for the Database CRUD Variables calls (with read operation) from the server to the offline storage layer. Thus, data gets accumulated as the user uses the app.
Following table details the behavior of various configurations (see Offline Data Support - Implementation for more details):
| Data Configuration | Data packed in installer | Data pulled from server | Saves data response from server | Editable in offline |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bundle with installer | Yes | Yes (if Delta Field is present) | Yes | No |
| Bundle with installer + on-demand sync | Yes | Yes (if Delta Field is present) | Yes | Yes |
| Sync data on-demand | No | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Cache data response | No | No | Yes | No |
Accumulating data received for the Database CRUD Variables calls (with read operation) from the server to the offline storage layer. Thus, data gets accumulated as the user uses the app.
Get data during app startup from the app-level Database CRUD Variables. The page level Database CRUD Variables are triggered only when the user visits the page. Unless the user visits a page once, data required for that page will not be available in offline. Say an app has with pages for employee and department details. The user opened the app and visited department page and closed the app. In offline mode, the user sees department page alone and employees page is not available as offline data for employees is not available. To deal with such scenarios, required data needs to be retrieved during app startup. The disadvantages are of this method are:
- the maximum number of records that can be pulled is limited to application limit of maximum records per request;
- app performance and responsiveness degrade during app startup, depending on the total number of records to be fetched.
_Data bundled along with the installer (apk or ipa) _is always available for offline. When an app requires data that does not change for at least 30 days, then instead of getting it from the server, data can be packaged along with installer. There are two advantages of this approach:
- No network request required and
- Improves app startup time - if this constant data is in hundreds of records, then downloading this huge amount of data during app startup or through Database CRUD API variable will slow the app.
The disadvantages of this method are:
- Bundled data cannot be edited or deleted.
- If the bundled data needs to be updated, then a new version of the app with updated bundled data has to be released.
How Sync Layer Works
During app startup, data (except bundle data) is removed and fresh data is pulled from the server. During pushing of offline data changes, if any push fails due to any reason, then the push will be attempted again in the next cycle.
When sync call of a particular entity fails due to any reason, then all subsequent calls to that entity and entities that are dependent upon it are blocked. Rest of the calls from the queue are pushed. All failures are removed from the queue but are persisted. There is no default UI support for error handling. But you can build UI using the data exposed through device variable.
For Example: In HR app, an employee object is dependent on the department. There are 3 departments (D1, D2, D3) and 3 employees (E1, E2, E3). E1 belongs to D1, E2 belongs to D2 and E3 belongs to D3. Following is the sync queue with some operation on these entities. Assume that boxes in red have failed at the server.
Following is the result.
- D1 call executed successfully.
- D2 failed by the server.
- D3 call executed successfully.
- E1 call executed successfully.
- E2 blocked as it is dependent of D2 which has an earlier failure (see 2).
- E3 failed by the server.
- E1 call executed successfully.
- E3 blocked because of earlier failure (see 6).
- E2 blocked because of earlier failure (see 5).
- D3 call executed successfully.
- D1 call executed successfully.
How Conflicts are Resolved
Currently, there is no conflict resolution strategy provided by WaveMaker. The last request will always override the data existing on the server.
For Example, Let's say there are two users working on a record say R.
- User1 reads R of version V1 and goes offline.
- User1 updates R (V2) in offline.
- User2 reads R of version V1 and modifies R (V3) in online. The latest version of R on the server is V3.
- User1 comes online and pushes his changes. So, the latest version of R on the server is V2. That is User1 changes override User2 changes.
- Ideally, whether User1 changes should be accepted or not depends on the business case. But, this option is currently not available and the last request prevails.
What happens to my offline changes when app is upgraded
Offline data changes persist across app upgrades. Let us say that a user installed the app (Version V1). In offline, he made some changes and closed the app. Then, Version V2 is released on play store or app store. Due to automatic upgrades, the app gets upgraded to V2. Now, when the user opens the app, it comes online with Version V2 and the offline data changes done in V1 is pushed to the server.